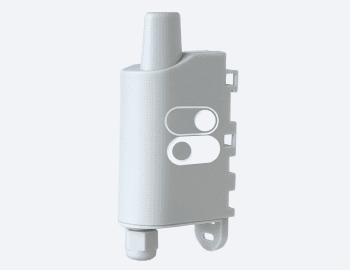
Understanding the nuances of electrical components is essential for effective system integration in your building. One such component is the dry contact, a term that often arises in discussions about building automation and control systems. Here, we demystify dry contacts, differentiate them from wet contacts, and explore their applications in enhancing smart buildings.
What Are Dry Contacts?
A dry contact refers to a set of switch contacts that are electrically isolated from the power source driving the device, such as a relay or a building management system (BMS). In simpler terms, activating a dry contact doesn't supply voltage or current by itself; instead, it relies on an external power source to function. This isolation ensures that the control side of a system remains separate from the load side, providing flexibility and safety in various applications.
Dry Contacts vs. Wet Contacts
Dry Contacts vs. Wet Contacts
The main distinction between dry and wet contacts lies in their connection to power sources:
Dry contacts do not supply power on their own; they merely act as a bridge, allowing an external voltage to pass through when closed. This feature is particularly useful when integrating systems that operate on different voltage levels or when electrical isolation is required.
Wet contacts are internally connected to a power source within a device. When activated, they supply a specific voltage to the output. While this can simplify wiring and reduce the need for external power supplies, it offers less flexibility, especially when different voltage levels are involved.
Applications in Smart Buildings
Applications in Smart Buildings
Incorporating dry contacts into smart building infrastructures offers numerous advantages, such as enhanced versatility through their interfacing with various systems, regardless of their operating voltages, being that dry contacts are volt-free. This makes them ideal for integrating legacy systems with modern automation.
By maintaining electrical isolation between control and load circuits, dry contacts reduce the risk of electrical interference and potential hazards, guaranteeing safer operation of building systems.
Devices equipped with dry contacts, like the Adeunis Dry Contacts sensor, enable remote status monitoring and control of equipment. This capability is ideal for efficient building management, allowing for real-time responses to system changes.
Practical Uses for Dry Contacts
The implementation of devices with a dry contact in smart buildings can be seen in various scenarios, like access and security management for the monitoring of doors and windows, providing immediate alerts if an entry point is opened unexpectedly, which will enhance security protocols; equipment monitoring for critical machinery to allow facility managers to receive up-to-date notifications on malfunctions, facilitating prompt maintenance actions and reducing downtime; and in environmental control to automate adjustments to systems like HVAC based on occupancy in a given room, or environmental conditions - devices like the Adeunis temperature sensor can help with this - optimising energy consumption and maintaining occupant comfort.
Incorporating dry contacts into your smart building infrastructure enhances operational efficiency and provides a flexible and safe method to integrate diverse systems. By understanding and incorporating the distinctions between dry and wet contacts, building developers and managers can make informed decisions that align with their automation and control objectives.